‘The debt-to-income (DTI) ratio is a personal finance measure that compares an individual’s debt payment to his or her overall income.’ The debt-to-income ratio is one way lenders, including mortgage lenders, measure an individual’s ability to manage monthly payment and repay debts. DTI is calculated by dividing total recurring monthly debt by gross monthly income, and it is expressed as a percentage.’ (Murphy, 2019)
In alphabetical order
D
Decision-making
‘The process of making choices by identifying a decision, gathering information, and assessing alternative resolutions’ (FYCM, n.d.)
D
Declared monuments
‘Hong Kong has many monuments which need proper preservation. In accordance with the Antiquities and Monuments Ordinance, the Antiquities Authority may, after consultation with the Antiquities Advisory Board and with the approval of the Chief Executive, by notice in the Gazette, declare a place, building, site or structure as a monument. The Antiquities Authority is then empowered to prevent alterations, or to impose conditions upon any proposed alterations as she/he thinks fit, in order to protect the monument’ (Antiquities and Monuments Office, 2019).
D
Deliberative democracy
D
Density gradient
The density gradient is defined as ‘percentage change in density per additional mile from the city center.’ (O'Sullivan, 2012, p.170)
D
Deontology
D
Design for Disassembly (DFD)
D
Design with nature
‘The way we occupy and modify the earth is best when it is planned and designed with careful regard to both the ecology and the character of the landscape’ (Weller et al., n.d.).
D
Development control
- An urban management process that ‘ensures the persistent growth and management of settlements with orderliness, improved settlement reflection, healthy and aesthetics. It also ensures that the environmental challenges as a result of settlement growth can be reduced to bearable levels’ (Vivan, Kyom, Balasom, 2013)
- The process of considering and granting or refusing permission for development. (Huxley, 2009, p.193)
D
Developmentalism
Developmentalism is a wide-ranging and complex philosophical position that sustains the idea of development – understood to be modernization as Westernization as a normative goal (Watts, 2009).
D
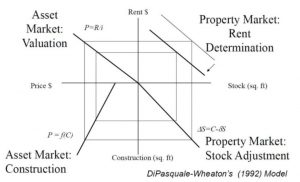
DiPasquale-Wheaton Four-Quadrant Model
D
Discourse
This concept is ‘often used to vaguely refer to spoken and written language while at other times it includes all forms of representation and refers quite specifically to theories derived from the work of post-structuralism in general and the work of Michel Foucault in particular. Foucault’s theory of discourse concerns how we know what we know, where knowledge comes from, who is authorized to profess it and how, ultimately, “truth” is established’ (Cresswell, 2009, p.211).
D
Disrupted city
Urban life suffers from the failure of urban infrastructures as the infrastructural disruption ‘tends to cascade between different networks and across geography and time in highly unpredictable and nonlinear ways’ (Graham, 2010, pp.25).
D
Distribution cost
‘The cost of transporting the firm’s output from the production facility to the output market.’ (O'Sullivan, 2012, p.38)
D
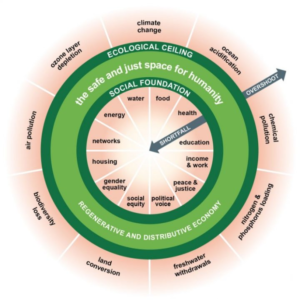
Doughnut economics
Reference List
Antiquities and Monuments Office (2019). Declared Monuments in Hong Kong. Retrieved from https://www.amo.gov.hk/en/monuments.php
Bächtiger, A., Dryzek, J., Mansbridge, J., & Warren, M. (2018). Deliberative Democracy: An Introduction. In The Oxford Handbook of Deliberative Democracy. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. Retrieved from https://www.oxfordhandbooks.com/view/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780198747369.001.0001/oxfordhb-9780198747369-e-50.
Cresswell, T. (2009). Discourse. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 211-214. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-008044910-4.00940-8.
DeSalvo, J.S. (2007). Teaching the DiPasquale-Wheaton Model, p.7. Retrieved from http://economics.usf.edu/PDF/Teaching%20the%20DiPasquale-Wheaton%20Model.pdf
FYCM (n.d.) Decision Making Process. Retrieved from https://www.umassd.edu/fycm/decision-making/process/.
Graham, Stephen. (2010). Disrupted cities: When infrastructure fails. New York: Routledge. 9(1). 1-26. Retrieved from https://www-taylorfrancis-com.easyaccess1.lib.cuhk.edu.hk/books/e/9780203894484
Huxley, M. (2009). Planning, Urban. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, Elsevier: Tokyo and Amsterdam, p.193-198.
Li, Susie (2015). ‘DfD Buildings: What is Design for Disassembly?’. Poplar. Retrieved from https://www.poplarnetwork.com/news/dfd-buildings-what-design-disassembly
Murphy, C.B. (2019). Debt-To-Income Ratio – DTI. In Investopedia. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/terms/d/dti.asp
O’Sullivan, A. (2012). Urban economics (8th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Raworth, Kate. (2017). ‘What on Earth is the Doughnut?’. Kate Raworth – Exploring doughnut economics [Blog]. Retrieved from https://www.kateraworth.com/doughnut/
The Ethics Centre. (2016). Ethics Explainer: Deontology. Retrieved from https://ethics.org.au/ethics-explainer-deontology/.
Thormark, Catarina. (n.d.). Motives for design for disassembly in building construction. Retrived from https://www.irbnet.de/daten/iconda/CIB11732.pdf
Utopia and Dystopia. (2019). Dystopia Definition – Meaning and Concepts of Dystopia. Retrieved from http://www.utopiaanddystopia.com/dystopia/dystopia-definition/
Vivan, E. L., Kyom, B. C. & Balasom, M. K. (2013). The Nature, Scope and Dimensions of Development Control, Tools and Machineries in Urban Planning in Nigeria. International Journal of Innovative Environmental Studies Research 1 (1), p.48-54.
Watts, M. (2009). Developmentalism. In International Encyclopedia of Human Geography, 123-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-008044910-4.00678-7
Weller, R., Steiner, F. & Fleming, B. (n.d.). What Does it Mean to Design with Nature now? Retrieved from https://mcharg.upenn.edu/conversations/what-does-it-mean-design-nature-now.